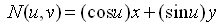8.9.3.29 IfcCylindricalSurface(圆柱面)
8.9.3.29.1 语义定义(Semantic definition)
圆柱面是在 z 方向上无界的表面。有界圆柱面通过使用 IfcBoundedSurface 的子类型来定义,其中 BasisSurface 为圆柱面。
继承属性的解释如下:
- SELF\IfcElementarySurface.Position 定义圆柱面的位置和方向。
- SELF\IfcElementarySurface.Position.Location 定义圆柱面轴上的一个点。
- SELF\IfcElementarySurface.Position.P[3] 定义圆柱面轴的方向。
C = Position.Location x = Position.P[1] y = Position.P[2] z = Position.P[3] R = Radius表面参数化如下:其中参数范围为 -∞ < u,v < ∞。
Figure 8.9.3.29.A 在上述参数化中,单位向量 z 的长度单位与半径 R 相同。在上面定义的放置坐标系中,表面由方程 S = 0 表示,其中
表面上任意点处表面的法向正方向由下式给出:
Figure 8.9.3.29.B ,或作为单位法向由
Figure 8.9.3.29.C Figure 8.9.3.29.D 法向方向远离圆柱体的轴线。
8.9.3.29.2 实体继承(Entity inheritance)
-
- IfcSurface
- IfcAnnotationFillArea
- IfcBooleanResult
- IfcBoundingBox
- IfcCartesianPointList
- IfcCartesianTransformationOperator
- IfcCsgPrimitive3D
- IfcCurve
- IfcDirection
- IfcFaceBasedSurfaceModel
- IfcFillAreaStyleHatching
- IfcFillAreaStyleTiles
- IfcGeometricSet
- IfcHalfSpaceSolid
- IfcLightSource
- IfcPlacement
- IfcPlanarExtent
- IfcPoint
- IfcSectionedSpine
- IfcSegment
- IfcShellBasedSurfaceModel
- IfcSolidModel
- IfcTessellatedItem
- IfcTextLiteral
- IfcVector
8.9.3.29.3 特性(Attributes)
| # | 特性(Attributes) | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IfcRepresentationItem (2) | |||
| LayerAssignment | SET [0:1] OF IfcPresentationLayerAssignment FOR AssignedItems |
将表示项分配给单个或多个层。LayerAssignments 可以覆盖其所在的 IfcRepresentation 的 Items 列表中的 LayerAssignments。 |
|
| StyledByItem | SET [0:1] OF IfcStyledItem FOR Item |
引用为表示提供表现信息的 IfcStyledItem,例如,为几何曲线提供曲线样式,包括颜色和厚度。 |
|
| IfcSurface (1) | |||
| * | Dim | IfcDimensionCount |
此属性是形式化派生的 IfcSurface 的空间维度。它始终是三维几何表示项。 |
| IfcElementarySurface (1) | |||
| 1 | Position | IfcAxis2Placement3D |
曲面的位置和方向。该属性用于定义曲面的参数化。 |
| 点击显示 4 个隐藏的继承特性 点击隐藏 4 个继承特性 | |||
| IfcCylindricalSurface (1) | |||
| 2 | Radius | IfcPositiveLengthMeasure |
圆柱面的半径。 |
8.9.3.29.4 形式化表示(Formal representation)
ENTITY IfcCylindricalSurface
SUBTYPE OF (IfcElementarySurface);
Radius : IfcPositiveLengthMeasure;
END_ENTITY;